Return Flow Impeders
Return Flow Impeders Specification
- Features
- Ferrite technology, high frequency compatibility, replaceable sleeve
- Power Source
- Passive/None required
- Sensors Specification
- Not Included
- Thermal Conductivity
- High
- Components
- Ferrite core, heat-resistant sleeve, end fittings
- Usage
- High-frequency induction welding pipe mills
- Response Time
- Instantaneous magnetic response
- Operating Temperature
- Up to 140C
- Product Type
- Return Flow Impeder
- Application
- Tube/Pipe manufacturing, return flow reduction in induction welding
- Size
- Available from 15mm to 250mm OD
- Dimension (L*W*H)
- Length: 180-1200 mm; OD: as per pipe size
- Function
- Restricts return flow in tube welding processes
- Color
- Black
- Weight
- Approx. 120-150 g each
- Capacity
- Supports various pipe sizes and speeds
- Thickness
- Typically 3-10 mm core ferrite; sleeve thickness varies
- Frequency
- Suitable for HF: 200 kHz - 500 kHz
- Temperature Resistance
- Maintains magnetic properties at elevated temperatures
- Core Material
- Manganese-zinc ferrite (MnZn ferrite)
- Magnetic Permeability
- Highcritical for efficient welding
- Sleeve Material
- Heat-resistant fiberglass/ceramic-coated sleeve
- Lifespan
- Multiple shifts depending on operating conditions
- Corrosion Resistance
- Good, due to coated sleeves and ferrite
- Shape
- Cylindrical with central bore
- Installation
- Fitted inside tube/pipe during welding
- Maintenance
- Minimalperiodic visual inspection recommended
- Customization
- Customized as per mill/pipeline OD and application
About Return Flow Impeders
Return Flow Impeders are utilised in situations where the interior of the tube must remain as dry as practicable. Return flow impeders may provide more resistance to coolant flow than through-flow kinds, necessitating a greater coolant pressure. Under typical working situations, a minimum pressure of 80 Psi enables appropriate cooling. Inlet temperature, weld power, frequency, and weld area shape all influence coolant flow needs. Moreover, when employing Return Flow Impeders, it is best to use clean, filtered coolant.
Enhance Welding Efficiency with Quality Impeders
By utilizing high-permeability MnZn ferrite and durable, heat-resistant sleeves, these return flow impeders improve the efficiency of high-frequency induction welding in tube and pipe mills. Their superior magnetic and thermal properties help minimize heat loss while promoting consistent welds, even under demanding production speeds and elevated temperatures.
Customizable for Diverse Applications
Impeders are available in numerous sizes (from 15mm to 250mm OD, lengths up to 1200mm), tailored to fit your specific tube/pipe dimensions and operational requirements. Their modular construction-including replaceable sleeves and end fittings-simplifies installation and maintenance, ensuring seamless integration into your welding line.
FAQ's of Return Flow Impeders:
Q: How are return flow impeders installed in tube and pipe welding applications?
A: Return flow impeders are inserted into the tube or pipe with their central bore aligned to the workpiece before the welding process begins. They are custom-fitted to match the outer diameter and length required by your specific mill or pipeline setup for optimal performance.Q: What is the function of manganese-zinc ferrite in impeders during induction welding?
A: Manganese-zinc ferrite provides high magnetic permeability, which helps restrict unwanted magnetic return flow within the tube during high-frequency induction welding. This improves energy efficiency and promotes consistent, high-quality welds.Q: When should return flow impeders be replaced or inspected?
A: Impeders typically last for multiple shifts, depending on the operating conditions and environment. Regular periodic visual inspections are recommended to check for signs of wear or sleeve degradation and ensure continued performance.Q: Where are these return flow impeders commonly used?
A: These impeders are predominantly used in high-frequency induction welding pipe mills throughout the tube and pipe manufacturing industry, supporting applications that require efficient return flow restriction under high-temperature and high-frequency conditions.Q: What benefits do heat-resistant sleeves provide for these impeders?
A: Heat-resistant fiberglass or ceramic-coated sleeves enhance the impeder's ability to maintain its magnetic properties at temperatures up to 140C. They also offer good corrosion resistance, thereby extending service life and reducing maintenance frequency.Q: How do customized impeders improve the tube welding process?
A: Customized impeders ensure precise fitting within your specific tubing dimensions and application needs, leading to better restriction of return magnetic flow. This accuracy optimizes welding efficiency, minimizes energy loss, and contributes to superior weld quality.Q: What is the typical process for changing or maintaining impeders during welding operations?
A: Maintenance is minimal and usually involves periodic visual checks for wear on the core and sleeve. Sleeves are designed to be replaceable, so worn units can quickly be swapped out during scheduled maintenance to minimize downtime.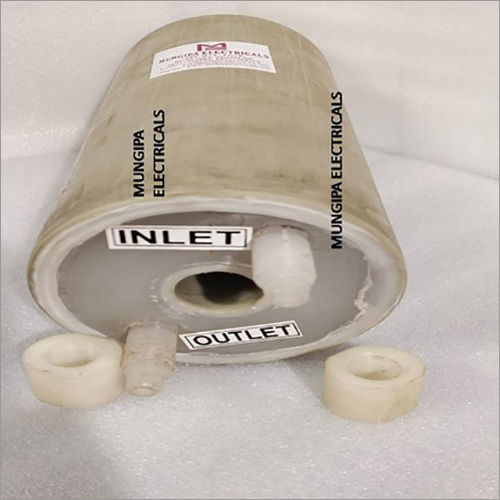
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
More Products in Ferrite Rod Category
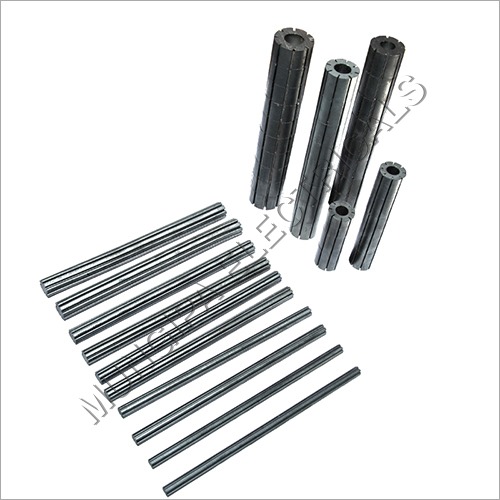
Ferrite Rod
Price 50 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 12 Pieces
Size : Standard
Application : HF WELDERS, TUBE MILLS
Color : BLACK
Warranty : Yes
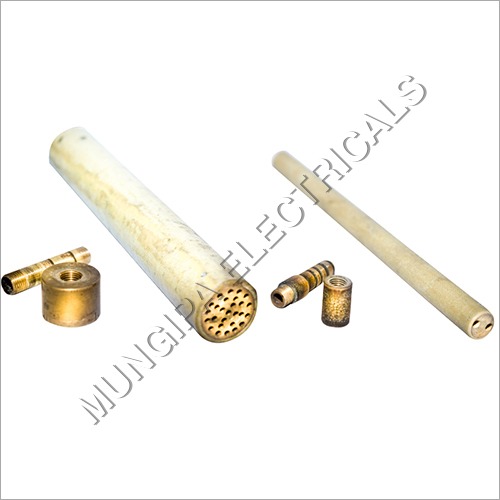
Ferrite Impeder Rod
Price 20 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 50 Pieces
Size : Standard
Application : Electrical Industry
Color : Multicolor
Warranty : Yes
Impeder Jacket Casing
Minimum Order Quantity : 10 Pieces
Size : Standard
Application : Electrical Industry
Color : Multicolor
Warranty : Yes
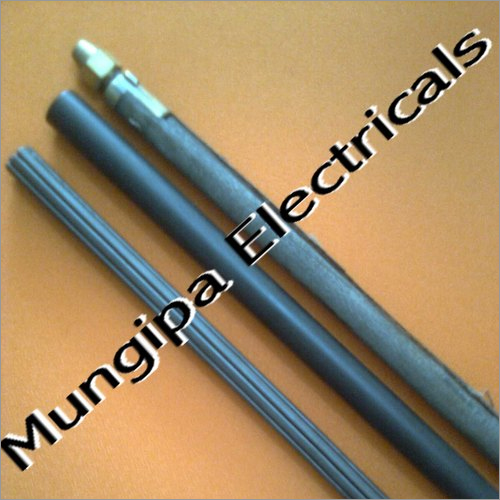
Impeder Rod
Minimum Order Quantity : 10 Pieces
Size : Standard
Application : Electrical Industry
Color : Multicolor
Warranty : Yes


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry





 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free